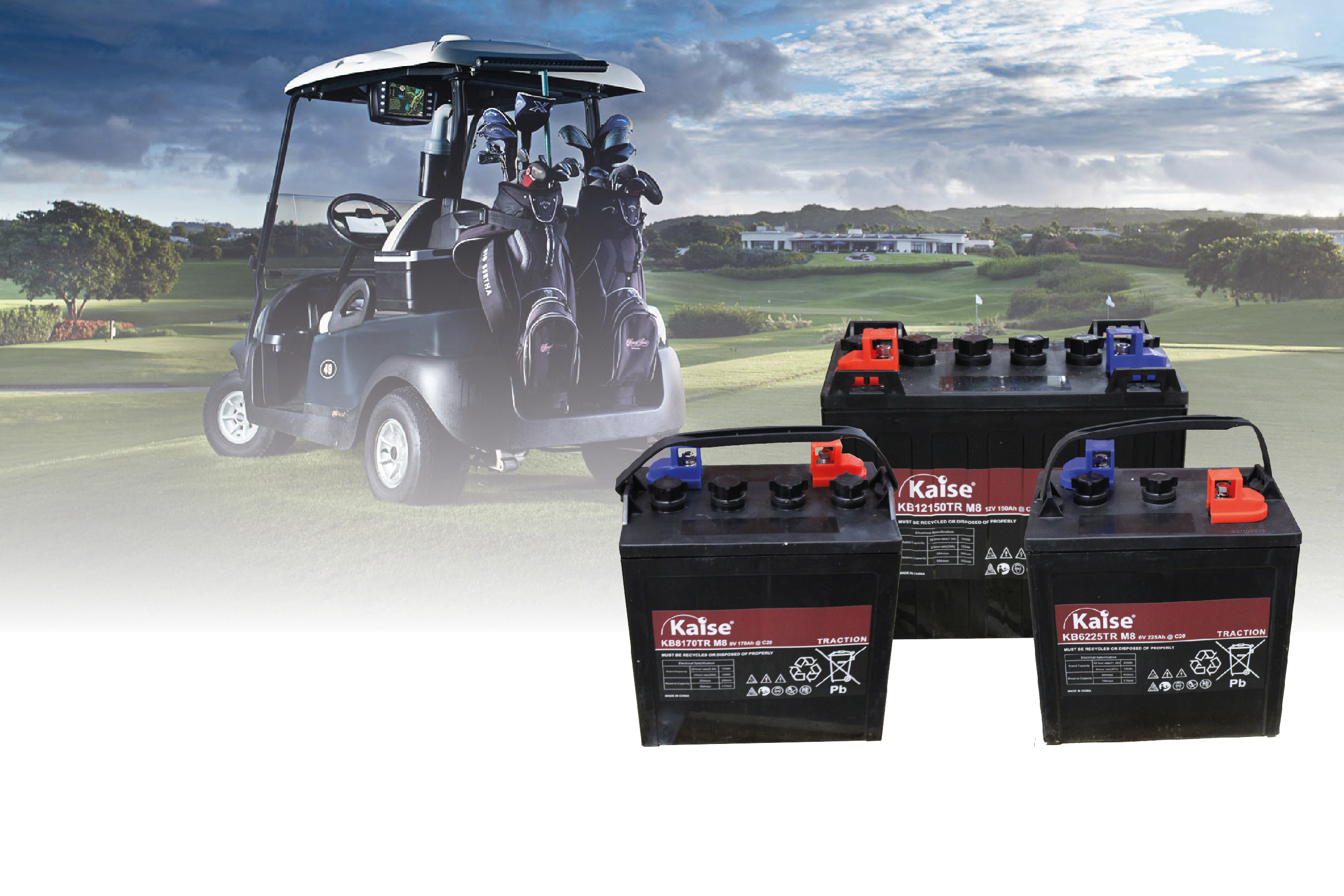
VRLA AGM
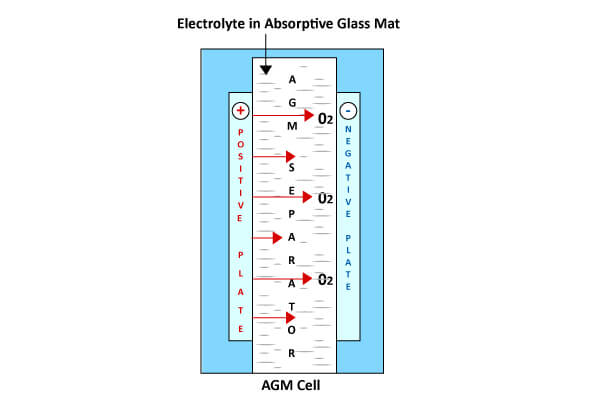
VRLA (Valve Regulated Lead Acid ) uses AGM technology (glass fibre separators). AGM separators separate the positive and negative plates by absorbing the electrolyte. The immobilisation of the electrolyte in the AGM separator maintains firm contact between the plates; this is a fundamental requirement for VRLA batteries. The use of the AGM Separator facilitates the transfer of oxygen gas generated on the positive plate during charging to the negative plate. During the chemical reaction of the internal recombination of the gases the hydrogen and oxygen creates water again, thus preventing its loss from the electrolyte.
Differences between VRLA batteries and traditional liquid electrolyte batteries
- Liquid electrolyte batteries do not have special sealed and pressurised valves, as they do not work on the recombination principle (gases escape from inside the battery during charging).
- Contains liquid electrolyte which may spill / flow and cause corrosion if dropped or punctured. Therefore, they are not transportable by air without special containers.
- They may only be installed “upright” and the “acid protection” must be maintained at the same time.
- As liquid electrolyte batteries lose gas during charging, maintenance is required.
- As the electrolyte can flow, “electrolyte replenishment” occurs and needs more overcharge to mix.